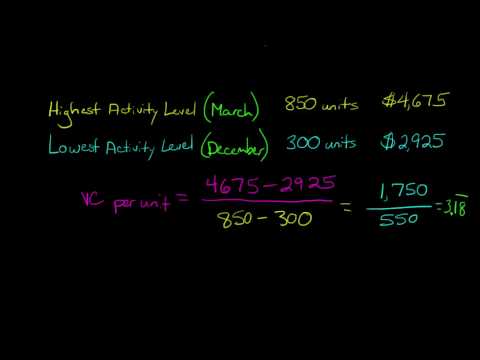The High Low Method for analyzing mixed costs in accounting
Share your inquiries now with community members
Click Here
Sign up Now
Lessons List | 9
Lesson
Comments
Related Courses in Business
Course Description
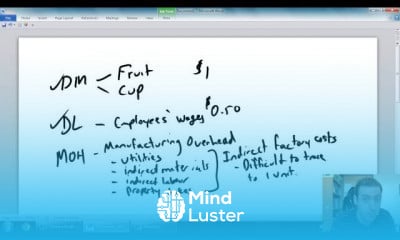
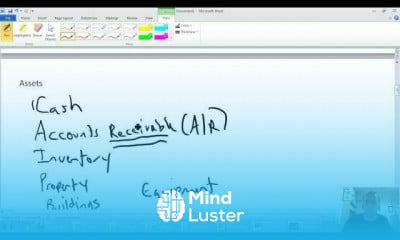
Cost behavior is the manner in which expenses are impacted by changes in business activity. A business manager should be aware of cost behaviors when constructing the annual budget, to anticipate whether any costs will spike or decline.What are the different types of cost behavior?
There are four basic cost behavior patterns: fixed, variable, mixed (semivariable), and step which graphically would appear as below. The relevant range is the range of production or sales volume over which the assumptions about cost behavior are valid. Often, we describe them as time-related costs.What is an example of cost behavior?
The change in total costs in response to the change in some activity. For example, some of the costs of owning and operating a vehicle will increase in total with an increase in miles driven. These are referred to as variable costs and include gasoline and tires.How do you determine cost behavior?
Definition of Cost Behavior
The total amount of a variable cost increases in proportion to the increase in an activity. The total amount of a variable cost will also decrease in proportion to the decrease in an activity. Fixed costs.
Trends
French
Graphic design tools for beginners
Data Science and Data Preparation
Formation efficace à l écoute de l
Artificial intelligence essentials
Learning English Speaking
Electrical engineering for engineer
Essential english phrasal verbs
MS Excel
American english speaking practice
Build a profitable trading
Build a tic tac Toe app in Xcode
Python for beginners
Figma for UX UI design
Marketing basics for beginners
Web Design for Beginners
YouTube channel setup
Magento Formation Français
Computer science careers
ArrayLists in C for beginners
Recent
Data Science and Data Preparation
Growing ginger at home
Gardening basics
Ancient watering techniques
Grow mushrooms
Growing onions
Veggie growing
Bean growing at home
Growing radishes
Tomato growing at home
Shallot growing
Growing kale in plastic bottles
Recycling plastic barrel
Recycling plastic bottles
Grow portulaca grandiflora flower
Growing vegetables
Growing lemon tree
Eggplant eggplants at home
zucchini farming
watermelon farming in pallets