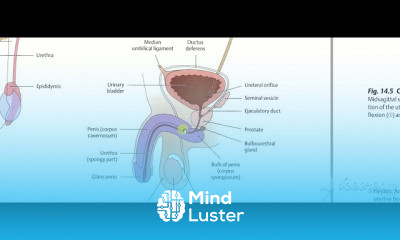
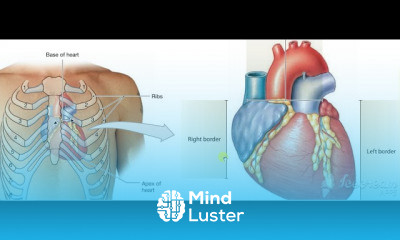
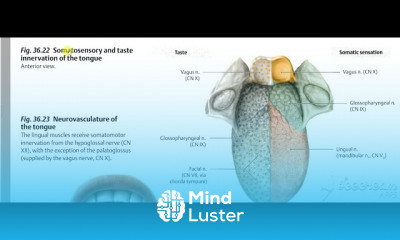
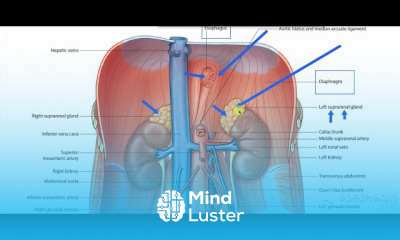
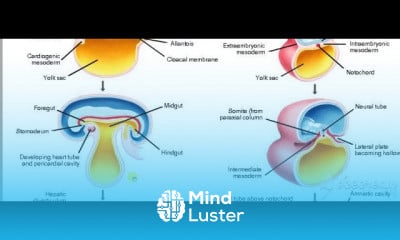
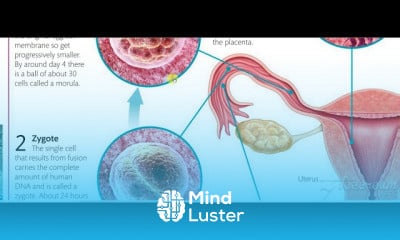
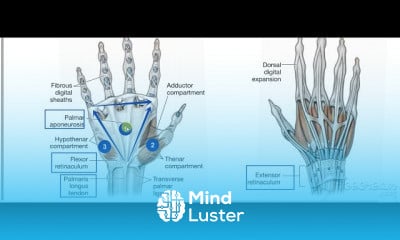
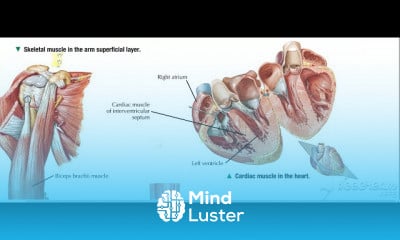
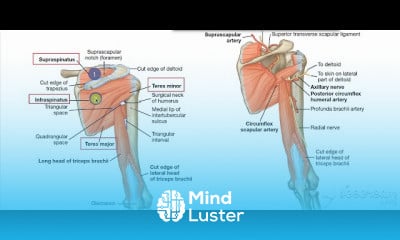
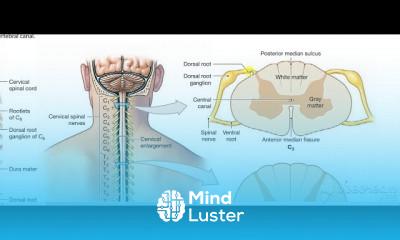
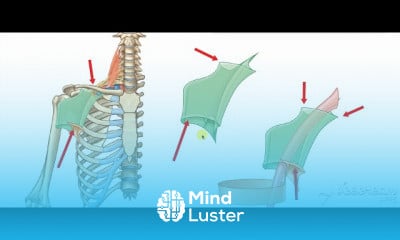
Gastric wall histology 6
Share your inquiries now with community members
Click Here
Sign up Now
Lessons List | 38
Lesson
Comments
Related Courses in Medical
Course Description
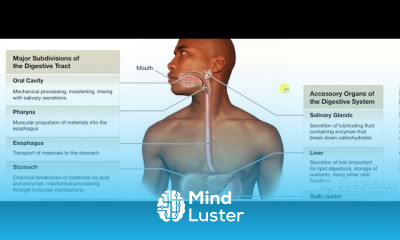
What is the digestive system?
Your digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and your liver, pancreas and gallbladder. The GI tract is a series of hollow organs that are connected to each other from your mouth to your anus. The organs that make up your GI tract, in the order that they are connected, include your mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus.
What does the digestive system do?
Your digestive system is uniquely constructed to do its job of turning your food into the nutrients and energy you need to survive. And when it’s done with that, it handily packages your solid waste, or stool, for disposal when you have a bowel movement.
Why is digestion important?
Digestion is important because your body needs nutrients from the food you eat and the liquids you drink in order to stay healthy and function properly. Nutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water. Your digestive system breaks down and absorbs nutrients from the food and liquids you consume to use for important things like energy, growth and repairing cells.
What organs make up the digestive system?
The main organs that make up the digestive system (in order of their function) are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus. Helping them along the way are the pancreas, gall bladder and liver.
Here’s how these organs work together in your digestive system.
Mouth
The mouth is the beginning of the digestive tract. In fact, digestion starts before you even take a bite. Your salivary glands get active as you see and smell that pasta dish or warm bread. After you start eating, you chew your food into pieces that are more easily digested. Your saliva mixes with the food to begin to break it down into a form your body can absorb and use. When you swallow, your tongue passes the food into your throat and into your esophagus.
Esophagus
Located in your throat near your trachea (windpipe), the esophagus receives food from your mouth when you swallow. The epiglottis is a small flap that folds over your windpipe as you swallow to prevent you from choking (when food goes into your windpipe). A series of muscular contractions within the esophagus called peristalsis delivers food to your stomach.
But first a ring-like muscle at the bottom of your esophagus called the lower esophageal sphincter has to relax to let the food in. The sphincter then contracts and prevents the contents of the stomach from flowing back into the esophagus. (When it doesn’t and these contents flow back into the esophagus, you may experience acid reflux or heartburn.)
Stomach
The stomach is a hollow organ, or "container," that holds food while it is being mixed with stomach enzymes. These enzymes continue the process of breaking down food into a usable form. Cells in the lining of your stomach secrete a strong acid and powerful enzymes that are responsible for the breakdown process. When the contents of the stomach are processed enough, they’re released into the small intestine.
Small intestine
Made up of three segments — the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum — the small intestine is a 22-foot long muscular tube that breaks down food using enzymes released by the pancreas and bile from the liver. Peristalsis also works in this organ, moving food through and mixing it with digestive juices from the pancreas and liver.
The duodenum is the first segment of the small intestine. It’s largely responsible for the continuous breaking-down process. The jejunum and ileum lower in the intestine are mainly responsible for the absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
Contents of the small intestine start out semi-solid and end in a liquid form after passing through the organ. Water, bile, enzymes and mucus contribute to the change in consistency. Once the nutrients have been absorbed and the leftover-food residue liquid has passed through the small intestine, it then moves on to the large intestine, or colon.
Pancreas
The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum that break down protein, fats and carbohydrates. The pancreas also makes insulin, passing it directly into the bloodstream. Insulin is the chief hormone in your body for metabolizing sugar.
Liver
The liver has many functions, but its main job within the digestive system is to process the nutrients absorbed from the small intestine. Bile from the liver secreted into the small intestine also plays an important role in digesting fat and some vitamins.
The liver is your body's chemical "factory." It takes the raw materials absorbed by the intestine and makes all the various chemicals your body needs to function.
The liver also detoxifies potentially harmful chemicals. It breaks down and secretes many drugs that can be toxic to your body.
Gallbladder
The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile from the liver, and then releases it into the duodenum in the small intestine to help absorb and digest fats.
Trends
French
Graphic design tools for beginners
Formation efficace à l écoute de l
Data Science and Data Preparation
Artificial intelligence essentials
Learning English Speaking
Essential english phrasal verbs
MS Excel
Electrical engineering for engineer
Build a profitable trading
American english speaking practice
Build a tic tac Toe app in Xcode
Design and Analysis of algorithms DAA
Python for beginners
YouTube channel setup
Marketing basics for beginners
Figma for UX UI design
Web Design for Beginners
Computer science careers
Magento Formation Français
Recent
Data Science and Data Preparation
Growing ginger at home
Gardening basics
Ancient watering techniques
Grow mushrooms
Growing onions
Veggie growing
Bean growing at home
Growing radishes
Tomato growing at home
Shallot growing
Growing kale in plastic bottles
Recycling plastic barrel
Recycling plastic bottles
Grow portulaca grandiflora flower
Growing vegetables
Growing lemon tree
Eggplant eggplants at home
zucchini farming
watermelon farming in pallets