Skin 2
Hide All Ads - Subscribe Premium Service Now
Share your inquiries now with community members
Click Here
Sign up Now
Lessons List | 13
Lesson
Comments
Related Courses in Medical
Course Description
A fascia is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. Fascia is classified by layer, as superficial fascia, deep fascia, and visceral or parietal fascia, or by its function and anatomical location.
Like ligaments, aponeuroses, and tendons, fascia is made up of fibrous connective tissue containing closely packed bundles of collagen fibers oriented in a wavy pattern parallel to the direction of pull. Fascia is consequently flexible and able to resist great unidirectional tension forces until the wavy pattern of fibers has been straightened out by the pulling force. These collagen fibers are produced by fibroblasts located within the fascia.
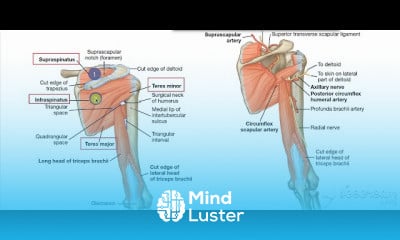
Fasciae are similar to ligaments and tendons as they have collagen as their major component. They differ in their location and function: ligaments join one bone to another bone, tendons join muscle to bone, and fasciae surround muscles and other structures.
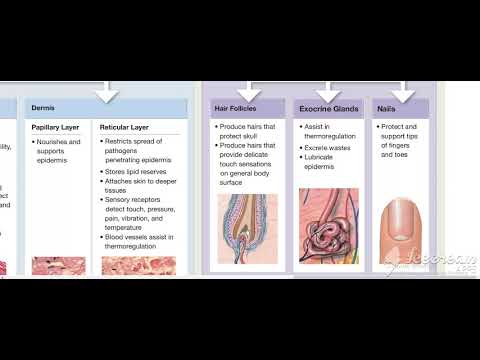
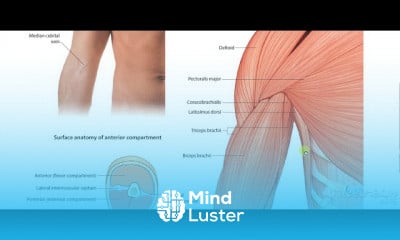
Superficial fascia is the lowermost layer of the skin in nearly all of the regions of the body, that blends with the reticular dermis layer It is present on the face, over the upper portion of the sternocleidomastoid, at the nape of the neck, and overlying the breastbone It consists mainly of loose areolar, and fatty adipose connective tissue and is the layer that primarily determines the shape of a body.[medical citation needed] In addition to its subcutaneous presence, superficial fascia surrounds organs and glands, neurovascular bundles, and is found at many other locations where it fills otherwise unoccupied space. It serves as a storage medium of fat and water; as a passageway for lymph, nerve and blood vessels; and as a protective padding to cushion and insulate.
Superficial fascia is present, but does not contain fat, in the eyelid, ear, scrotum, penis and clitoris.
Due to its viscoelastic properties, superficial fascia can stretch to accommodate the deposition of adipose that accompanies both ordinary and prenatal weight gain. After pregnancy and weight loss, the superficial fascia slowly reverts to its original level of tension.
Trends
Graphic design tools for beginners
MS Excel
Google Python class
Learning English Speaking
French language for beginners
Python programming language
ChatGPT high level
VLSI Physical Design basics
French
Design and Analysis of algorithms DAA
Excel fundamentals for finance
Data analysis in Python
Web Design for Beginners
YouTube channel setup
Formation efficace à l écoute de l
Electrical engineering for engineer
WordPress Complete Course in Hindi
Reading financial statements
Marketing basics for beginners
Embedded Systems ES
Recent
Logistic regression machine learning
Linear regression in python
Neural Network python
Optimization in deep learning
CNN in deep learning
Recurrent neural networks
Deep neural network python
Transformers in deep learning
Installing gitHub MCP
AI image generators
AI avatar animation
Figma MCP
Google A2A protocol
10X coding tools for developers
French language for beginners
Pronunciation sounds in french
French learning strategies
French vocabulary and sentences
French DELF A1 reading
French TEF exam



You must have an account within the platform in order to participate in the discussion and comment. Register now for freeClick here